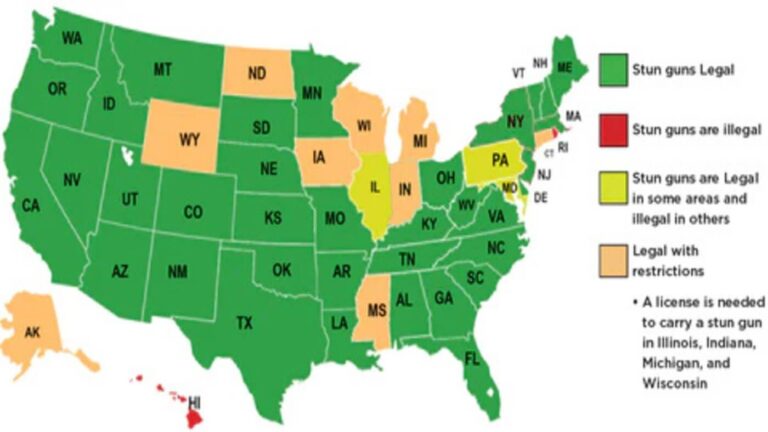
In recent years, the legal landscape surrounding stun gun ownership has undergone significant changes across the United States. As concerns about personal safety continue to rise, many states have revisited and revised their laws regulating the possession, carry, and use of stun guns. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the current state-by-state legal shifts, highlighting new regulations, emerging trends, and key considerations for consumers and policymakers alike. Understanding these changes is crucial for residents and legal experts navigating the evolving parameters of self-defense and public safety.
Table of Contents
- State-Level Variations in Stun Gun Legislation and Their Implications
- Understanding Restricted Zones and Compliance Requirements
- Navigating Permit Procedures and Age Limitations for Ownership
- Best Practices for Staying Informed on Legislative Updates and Ensuring Legal Use
- To Conclude
State-Level Variations in Stun Gun Legislation and Their Implications
Across the United States, lawmakers continue to reevaluate stun gun regulations, resulting in a complex mosaic of legal standards that vary significantly from state to state. Some states have enacted measures to loosen restrictions, enabling wider civilian access to these self-defense devices. For example, states like Texas and Florida have introduced legal amendments that ease permit requirements, underscoring a growing trend toward recognizing stun guns as a legitimate form of personal protection. Conversely, others maintain stringent controls or outright bans, reflecting ongoing concerns over public safety and potential misuse. These disparities foster environments where ownership rights and responsibilities can change drastically merely by crossing state lines.
The implications of this patchwork legislation extend beyond mere regulatory boundaries and shape the everyday realities of stun gun owners. Key impacts include:
- Legal Ambiguity: Travelers and residents alike face confusion regarding possession and usage rules, increasing inadvertent legal violations.
- Enforcement Challenges: Law enforcement agencies must adapt to varied statutes, complicating arrest protocols and prosecution consistency.
- Market Impact: Consumer access fluctuates with state policies-vendors adjust inventory and marketing to align with local laws.
This evolving landscape demands heightened awareness and compliance vigilance from stun gun owners, alongside continuous legislative monitoring by stakeholders.
Understanding Restricted Zones and Compliance Requirements
Stun gun regulations vary widely across different states, often reflecting unique concerns about public safety and law enforcement priorities. Certain areas are designated as restricted zones, where possession or use of stun guns is either prohibited or severely limited. These zones typically include government buildings, schools, airports, and public transportation hubs, where the potential risks of misuse are heightened. Individuals are advised to consult local laws before carrying stun guns in these sensitive environments to avoid heavy fines or legal action.
Compliance is not merely about avoiding restricted zones; it often involves adhering to state-specific registration, age restrictions, and even permit requirements. For instance, some states mandate a background check or a permit for stun gun ownership, while others impose restrictions on carrying them in concealed or open manners. To ensure compliance, users should:
- Verify whether the state requires a permit or registration
- Understand any transport restrictions when traveling between states
- Stay informed about recent legislative changes affecting stun gun legality
Navigating Permit Procedures and Age Limitations for Ownership
Understanding the varied landscape of stun gun ownership today requires close attention to the distinct permit procedures set forth by each state. While some jurisdictions demand a formal application process complete with background checks and mandatory training sessions, others allow possession only after local law enforcement approval. Notably, several states have implemented streamlined digital application platforms, facilitating quicker approvals but also introducing stricter compliance and record-keeping responsibilities for owners. Potential purchasers should prioritize consulting state-specific government resources to ensure conformity with permit requirements and avoid inadvertent legal pitfalls.
Age restrictions also play a crucial role in defining legal possession, with the minimum age threshold for stun gun ownership typically ranging between 18 and 21 years. Many states have instituted age-based prohibitions explicitly excluding minors, tying ownership eligibility to voter registration or military status in some cases. This variable mosaic of age limitations often intersects with permit eligibility, emphasizing the need for prospective buyers to verify their qualifications thoroughly before acquiring a stun gun. By staying informed about age restrictions and permitting nuances, citizens can better navigate the regulatory framework shaped by ongoing legislative revisions.
- Permit procedures may include background checks, application fees, and training requirements.
- Age limits typically set a minimum ownership age between 18 and 21.
- State-specific variations require careful review of local laws and enforcement policies.
Best Practices for Staying Informed on Legislative Updates and Ensuring Legal Use
To effectively navigate the constantly evolving landscape of stun gun legislation, staying proactive is essential. Regularly monitoring official state government websites, subscribing to legislative newsletters, and leveraging reputable legal databases can provide timely updates on new bills, amendments, and enforcement measures. Additionally, engaging with advocacy organizations specializing in self-defense laws can offer expert insights and alerts tailored to your state. Always verifying the sources of information ensures you avoid misinformation which could lead to inadvertent legal violations.
Ensuring compliance extends beyond knowledge; it requires diligent application of legal requirements such as obtaining necessary permits, abiding by age restrictions, and adhering to transportation and usage regulations. Consider implementing a checklist to review your stun gun ownership status annually, including confirmatory steps like re-certification or registration renewals where applicable. When in doubt, consulting with a qualified attorney can clarify nuances and mitigate risks associated with non-compliance. This disciplined approach is vital to legally wielding stun guns responsibly and confidently across different jurisdictions.
To Conclude
As legislation surrounding stun gun ownership continues to evolve across the United States, it remains crucial for both current and prospective owners to stay informed about the specific laws in their state. Understanding these legal changes not only ensures compliance but also contributes to responsible usage and overall public safety. Stakeholders, including lawmakers and advocacy groups, will likely play pivotal roles in shaping future regulations. Monitoring these developments will be essential for anyone navigating the complex landscape of self-defense laws moving forward.